Last Updated on December 26, 2022 by Mathew Diekhake
It’s no secret that Windows operating systems were often falling victim to virus attacks. Contrary to belief, no operating system out there isn’t susceptible to a virus—you would get them on Mac as well and just as often but there aren’t anywhere near as many people using the Mac operating system and therefore most of the time spent on trying to create viruses is done so for the Windows environment.
A modern-day version of Windows, such as Windows 10, is considerably more secure an operating system than the earlier versions such as Windows 7. Microsoft has come up with a solution to the viruses that were plaguing it in years past where Windows now requires programs and applications to be signed before the operating system will run them. And since a virus is something not welcomed by Microsoft, it’s about as close you can get to impossible to obtain one as you can get if you are up to no good.
You don’t just have to take Microsoft’s word for it that system files and drivers have been signed by them either; that information is available for you to check whenever you want by using the File Signature Verification tool.
Note: a system file or driver that is not signed doesn’t necessarily make it malicious. There are plenty of files out there that go unsigned and are yet as trustworthy as the signed ones. If you do find an unsigned file and want to keep it, then run it through VirusTotal before installing it on your computer just to be sure it’s safe. The main security feature that Windows rolls with is not allowing unsigned files to run before the operating system—that was the trick that malicious files needed to cause computers harm. Once the operating system is running, then your antivirus will stop it from causing the damage that it intended to carry out, provided that you don’t turn off your Windows Defender security (or the antivirus that you have replaced it with).
How to Verify if System Files and Drivers are Digitally Signed in Windows
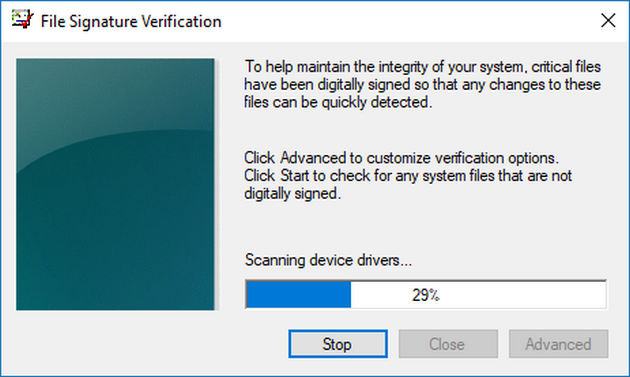
You can check that system files and drivers are digitally signed by using the File Signature Verification tool that is always available by default in Windows operating systems. To bring it up, hold the Windows logo + R keys and then type “sigverif” into the Run dialog box and hit the “OK” button. It’ll automatically bring up the front page of the tool.
You can start by clicking on the “Advanced” button if you want to change the logging settings.
Otherwise just click on the “Start” button instead to find any files that are not yet digitally signed.
It’ll run through the motions automatically from here on and let you know that it is scanning for device drivers. Just wait until the progress bar reaches the other side of the window.
Any files that have not yet been digitally signed will be listed in the window. You can also see the total number of signed files and unsigned files at the bottom of the window.
Viruses and malware were having a field day before Windows 8 came around and then Microsoft came up with the idea of having digital signatures to stop anything from being able to run before the operating system was booted up. It has made a huge difference. That combined with the default Windows Defender antivirus and the Malicious Software Removal Tool taking a huge leap forward and you should be able to use your computers that run Windows now with little trouble. If you did want extra protection though we recommend checking out Malwarebytes.
Related Tutorials